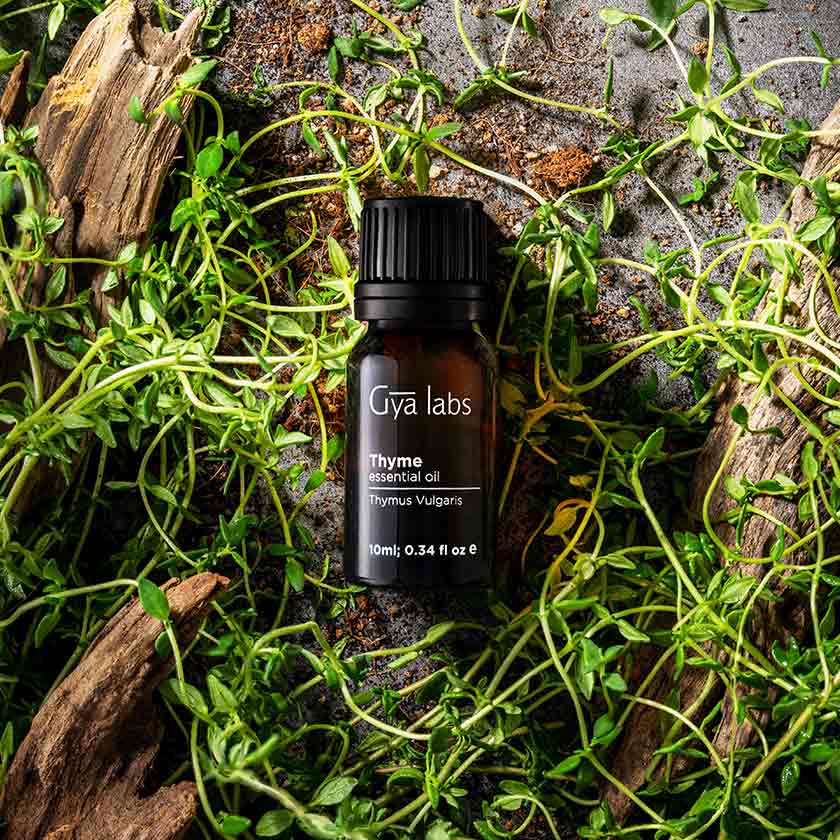
Thyme, a classic mint family herb, is not only a culinary staple in many areas of the world because of its distinctive flavour, but also a treatment because of its numerous health advantages. Thymus vulgaris is the scientific name for this plant, which is native to Western Asia and Europe.
- Thyme gets its name from the Latin term ‘thymus,’ which is derived from the Greek word ‘thumus,’ which means smoke,’ owing to its stimulating scent.
- To fight against airborne germs and microorganisms, ancient Greeks and Romans burnt this customary plant as incense in temples, houses, and sacred places for millennia.
- Thyme oil, known as a healer and protector, was also used as an antidote to protect people from poisoning, as a digestive aid, and as a cough and cold remedy. Ancient
- Egyptians also employed this essential oil to embalm corpses, believing that the incense of this aromatic herb was a strong assist to aid them in their eternal trip.
- Thyme was later introduced to the rest of the globe as a culinary and medicinal plant with several health advantages.
- Common thyme, red creeping thyme, caraway thyme, and lemon thyme are the four types of thyme.
Thyme Oil Uses
Several studies have demonstrated that thyme essential oil can decrease or eradicate foodborne germs, improve heart health, and reduce inflammation in the body, among other things.
Before you run out and buy a bottle, keep in mind that there’s no evidence that thyme oil will heal any specific ailment on its own.
While additional study is needed, thyme oil is presently regarded to be useful when taken in conjunction with other therapy programmes rather than as a stand-alone treatment or cure.
Thyme oil has a number of chemicals that are beneficial to one’s health.
Carvacrol, thymol, linalool, cineol, camphor, and borneol are some of these chemicals. These chemicals help improve the use of the oil, by providing beneficial properties required to make the oil useful. In most households, thyme essential oil is a staple in rooms such as the bedroom, bathroom and kitchen. It is important to understand its various uses in daily life.
Let’s have a look at how these chemicals can help with various thyme essential oil applications.
Acne
- Thyme oil uses expand to the realm of skincare and beauty.
- It has been shown to be useful in decreasing acne-causing germs on the skin.
- Both thyme and oregano oil were found to be beneficial in killing germs in an animal investigation, although oregano oil was more effective.
- Hence these are viable options that can be used in common households.
Alopecia areata
- Thyme essential oil, along with other essential oils and a carrier oil, can be used as a therapy to prevent hair loss when combined with massage.
- There is currently no evidence to suggest that thyme essential oil is useful for this ailment, while anecdotal evidence suggests that a mixture of essential oils, including thyme essential oil, may be effective.
Helps fight Breast cancer
- Wild thyme extract, according to one exploratory research, may one-day show potential in the battle against breast cancer.
Coughs and diseases of the respiratory tract
- The antispasmodic benefits of thyme oil are assumed to be due to the thymol component.
- Thyme essential oil, when combined with primrose, has been demonstrated to help relieve coughs and shorten the duration of respiratory tract infections like the common cold.
Preservative in food
- Thyme essential oil was shown to be helpful at eliminating food-related germs and fungus in research published in the Journal of Medicine and Life.
- Salmonella, Staphylococcus aureus, and Helicobacter pylori have all been proven to exhibit antibacterial properties in thyme and thymol.
Coronary artery disease or heart diseases
- Carvacrol in thyme essential oil was discovered to be an efficient anti-inflammatory agent with cardioprotective properties in a 2010 laboratory research published in the Journal of Lipid Research, making it potentially useful for persons with heart disease.
Oral hygiene can be improved
- Several investigations have shown that thymol has anti-inflammatory properties. Thymol, found in thyme oil, works to reduce inflammation and infection.
- Thymol’s anti-inflammatory and antibacterial qualities, according to a recent study, make it good for dental health.
- Several dental products, notably Listerine Cool Mint mouthwash, contain the chemical.
How to use thyme oil
Now that we have gone through the possible thyme oil uses, let’s figure out how to use it.
There hasn’t been any substantial study since a short 1998 aromatherapy experiment demonstrated positive outcomes for some persons with alopecia areata.
Because thyme essential oil is unlikely to damage you, you should give it a try and see how it works. If you want to give an aromatherapy scalp treatment a try at home, follow these steps:
- As the carrier oil, choose a vegetable oil such as jojoba or grapeseed oil.
- 3 to 5 drops each of thyme, lavender, rosemary, and cedarwood essential oils in 2 to 3 cups carrier oil Each of these oils contains characteristics that may help with hair development and scalp health.
- Every day, for about 10 minutes, massage a tiny bit into the scalp.
- Leave on for an hour or more, if desired.
- Rinse and condition with a gentle shampoo and conditioner.
- It may take many months for this therapy to take effect. If your scalp becomes irritated, stop using it.
Do a patch test with each oil before using it to make sure it doesn’t irritate your skin, eyes, or nasal passages.
Prior to testing, essential oils should always be combined with a carrier oil. Do not apply undiluted essential oil to your scalp or any other part of your body.
Conclusion
- Thyme oil uses have been proven to help with a variety of ailments as well as heart and mouth health. It isn’t intended to be used as a stand-alone treatment for any ailment, although it may be useful when taken in conjunction with other medicines.
- It is also present in commercially produced items such as cosmetics, toiletries, and meals, in addition to essential oil.
- It’s commonly used as a preservative and antibacterial agent.