Welcome to our comprehensive guide about the widespread use and implementation of wireless slip rings—an indispensable component bridging the communication gap between stationary and rotating mechanisms. Gaining popularity due to their reliability, longevity, improved performance, and minimal maintenance, wireless slip rings facilitate seamless transmission of data and power with the help of radio frequency signals. From the aerospace industry to telecommunications, find out more about the benefits, common models, fault remedies and FAQs related to this unique, contact-free solution.
What Is a Wireless Slip Ring?
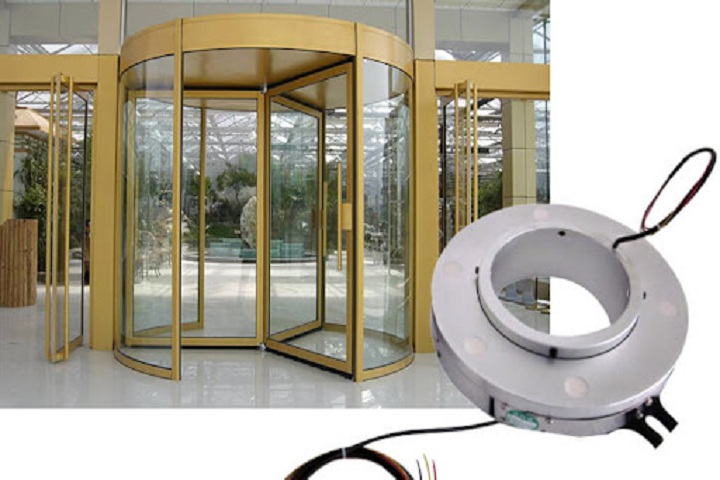
A wireless slip ring, also known as a rotary joint or radio frequency (RF) slip ring, is an electromechanical device that allows for the transmission of electrical signals between stationary and rotating parts of equipment. Unlike traditional slip rings that rely on physical contact via brushes and rings, wireless slip rings use radio frequency signals for data and power transmission, eliminating the need for physical connections.
Which Industries and Equipment Use Wireless Slip Rings?
Wireless slip rings are commonly used in various industries and equipment, including:
- Aerospace and Defense: Satellite antennas, radar systems, and missile guidance
- Manufacturing: Industrial robots, automated production lines, and rotating tables
- Renewable Energy: Wind turbines, solar power systems, and hydroelectric generators
- Medical: MRI machines, CT scanners, and robotic surgical equipment
- Telecommunications: Mobile communication towers, microwave dishes, and fiber optic rotary joints
Why Are Wireless Slip Rings Popular?
Wireless slip rings have gained popularity due to their numerous benefits over traditional slip rings, such as:
- Lower maintenance: Since there are no brushes or contact surfaces, wear and tear are significantly reduced, resulting in longer service life and reduced maintenance costs.
- Enhanced performance: Wireless slip rings provide improved signal integrity, reduced signal noise, and increased data transfer rates.
- Minimal interference: The non-contact nature of wireless slip rings reduces the likelihood of electrical interference, improving signal quality and system performance.
- Increased reliability: Wireless slip rings can operate in harsh environments and resist contamination, extending their operational life and enhancing reliability.
Common Models of Wireless Slip Rings
There are several common models of wireless slip rings, including:
- Capacitive slip rings: Utilize capacitive coupling to transmit signals and power across rotating joints.
- Inductive slip rings: Employ inductive coupling via magnetic fields for data and power transfer.
- Radio frequency slip rings: Rely on radio frequency signals for wireless transmission of data and power.
Wireless Slip Ring Accessories
Some useful accessories for wireless slip rings include:
- Antenna systems: Allow for higher gain, extended range, and increased signal reliability.
- Signal amplifiers: Improve signal strength and performance in high-noise or long-distance applications.
- Enclosures: Protect sensitive components from environmental factors and electromagnetic interference.
- Mounting brackets: Facilitate installation and integration of wireless slip rings in various equipment configurations.
Common Faults and Solutions of Wireless Slip Rings
Some potential faults and their corresponding solutions for wireless slip rings include:
1. Weak or intermittent signal:
- Ensure proper antenna alignment and orientation.
- Check whether there is any obstruction or interference.
- Utilize signal amplifiers to boost signal strength.
2. Excessive signal noise:
- Confirm proper grounding and shielding procedures are in place.
- Investigate the source of noise and implement appropriate countermeasures,
such as filtering or signal conditioning.
3. Data transfer issues:
- Verify the correct encoding/decoding schemes and protocols are being utilized.
- Consider upgrading to higher bandwidth models or adding additional channels if bandwidth limitations are encountered.
How to Replace the Wireless Slip Ring?
Replacing a wireless slip ring generally involves the following steps:
- Disconnect power and signal connections to the faulty slip ring.
- Remove any fasteners or mounting hardware securing the slip ring to the equipment.
- Carefully remove the faulty slip ring from the equipment.
- Install the new slip ring in the same orientation and position as the original.
- Secure the new slip ring with the appropriate fasteners or mounting hardware.
- Reconnect all power and signal connections to the new slip ring.
Frequently Asked Questions About Wireless Slip Rings Not Working
Can I use a wireless slip ring in a high-vibration environment?
Yes, wireless slip rings can operate in high-vibration environments; however, proper mounting and vibration isolation techniques may be required to ensure reliable performance.
How do I choose the right wireless slip ring for my application?
Consider factors such as the required data rates, signal types, operating environment, and equipment constraints when selecting a wireless slip ring.
What is the maximum operating temperature for wireless slip rings?
The maximum operating temperature for wireless slip rings varies depending on the specific model and manufacturer. Consult the product datasheet for temperature range specifications.
Are wireless slip rings susceptible to interference from other wireless devices?
While wireless slip rings are designed to minimize interference, it is essential to follow proper installation and signal management practices to avoid compromising performance.
Is there a specific way to maintain and clean wireless slip rings?
Unlike conventional slip rings, wireless slip rings require less maintenance due to lack of physical contact elements. They should be kept free from dust and debris for optimal performance. Regular inspection for signs of fault or degradation is recommended for maintaining their lifespan.
What should I do if my wireless slip ring is echoing or repeating signals?
Echoes or signal repetitions may indicate issues with signal interference or excessive ‘bounce’ in the transmission system. Inspect the slip ring for any damaged components or loose connections. Professionals should ideally address issues related to signal bouncing.
Can I use multiple wireless slip rings in proximity to each other?
Yes, multiple wireless slip rings can be used in proximity. However, care should be taken to avoid signal interference. Each slip ring should work on different frequencies or use shielding measures to prevent cross-talk.
How much power can a wireless slip ring transmit?
The power a wireless slip ring can transmit depends on its design, signal power, and frequency. For exact figures, consult the specifications provided by the manufacturer.
Can wireless slip rings be custom-made for specific applications?
Yes, some manufacturers offer custom solutions to cater to specific application requirements. These may include modifications in design, size, power handling, and signal characteristics based on the operational needs.
Do wireless slip rings have a minimum or maximum operating speed?
The operating speed of wireless slip rings varies significantly depending on the design and application. Some models can handle high rotational speeds while others are designed for slow, steady rotations. Always check the manufacturer’s guidelines for the appropriate operating speeds.
We trust that this guide has shed light on the essential role of wireless slip rings, providing you with a firm grasp over their operation and benefits across industries. As technology continues to evolve, expect robust contributions from these electromechanical devices, enhancing not only the safety and efficiency, but also the effectiveness of rotating machinery. So next time you encounter a wireless slip ring, remember its hidden, sophisticated operation that seamlessly bridges the gap between stationary and rotating parts, all without physical contact.